Built-in functions – Procedural noise functions
Basic noise
The basic noise function is Perlin noise, which is a pseudo-random noise function.
This is an example of Perlin noise used as a displacement value:
Returns single-valued (scalar) Perlin noise evaluated at x. Values returned lie in the range from -1 to 1.
Returns single-valued Perlin noise evaluated at x.
Returns single-valued Perlin noise evaluated at x.
Returns 3-valued noise (each component is a decorrelated noise value) evaluated at 2d-coordinates.
Returns 3-valued noise (each component is a decorrelated noise value) evaluated at 3d-coordinates.

An example of 3-valued noise.
Returns 4-valued noise (each component is a decorrelated noise value) evaluated at 2d-coordinates.
Returns 4-valued noise (each component is a decorrelated noise value) evaluated at 3d-coordinates.
Basic Fractional Brownian Motion noise
This type of noise is made by adding together a number of different frequences of Perlin noise together.

FBM, 1 Octave of noise.
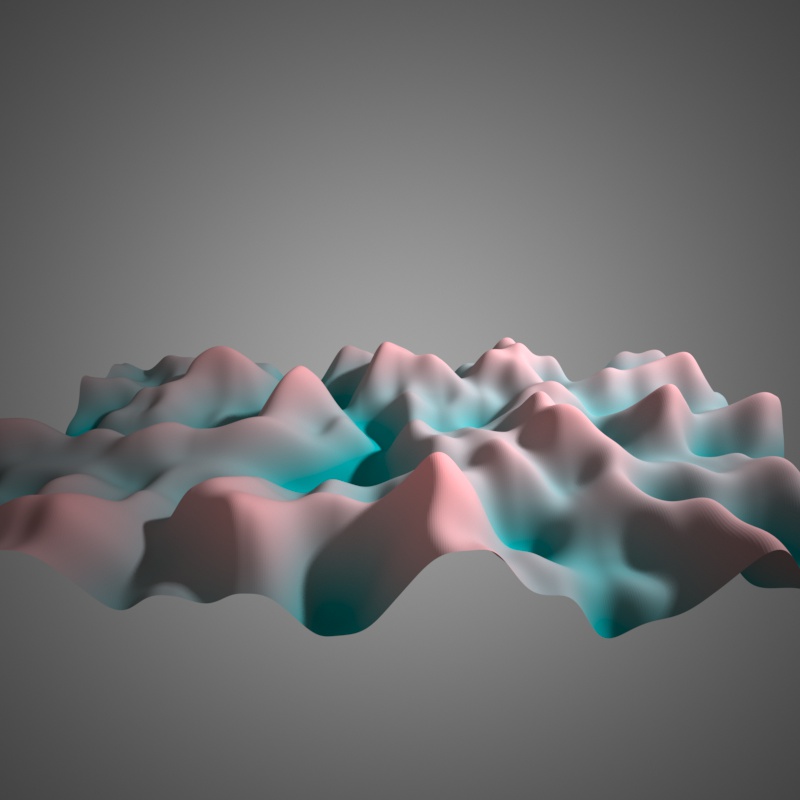
FBM, 2 Octaves of noise.
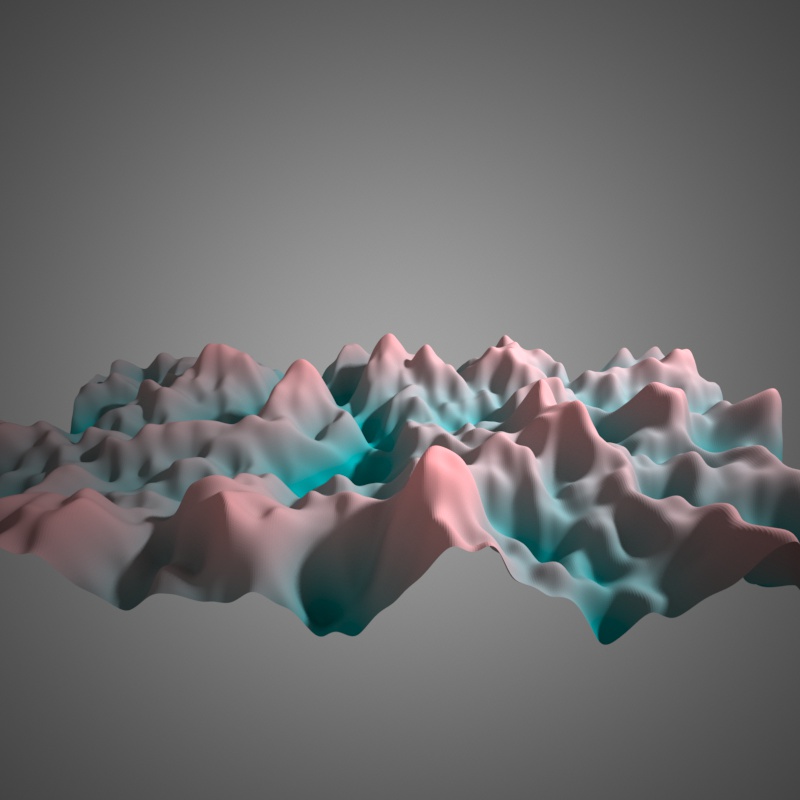
FBM, 3 Octaves of noise.
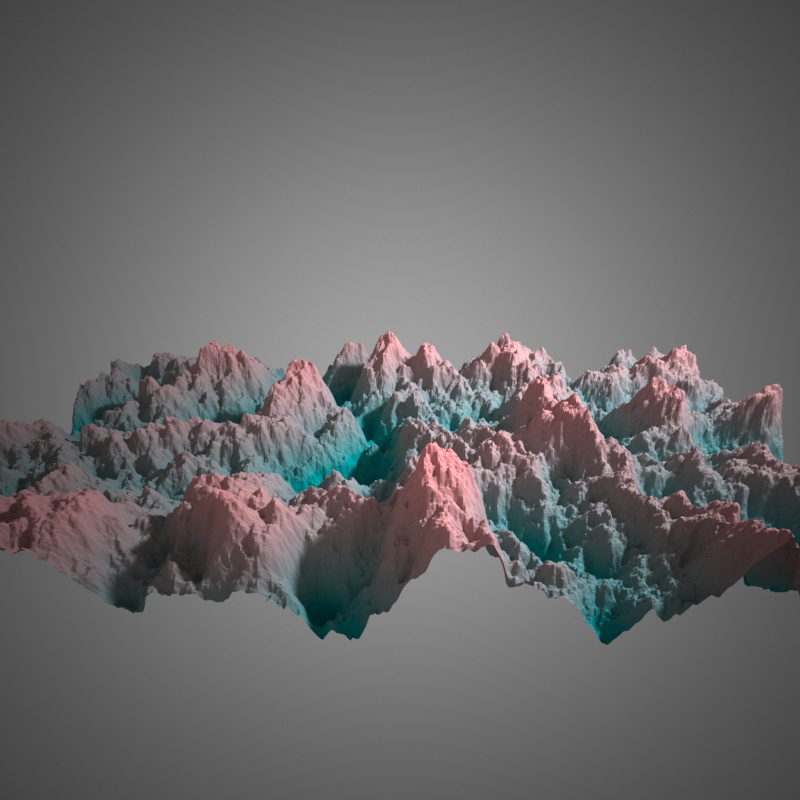
FBM, 10 Octaves of noise.
Returns oc octaves of 1-D Fractional Brownian Motion noise evaluated at x.
Returns oc octaves of 2-D Fractional Brownian Motion noise evaluated at x.
Returns oc octaves of 3-D Fractional Brownian Motion noise evaluated at x.
Grid noise
gridNoise(vec2 x) real
gridNoise(vec3 x) real
Takes the floor of the coordinates passed in, and then returns a quasi-random value between 0 and 1 for those integer coordinates.

Grid noise.
Voronoi noise
Returns the coordinates of the nearest Voronoi site.
The irregularity argument controls the 'randomness' of the site positions. It should lie in the range [0, 1].
Irregularity of zero corresponds to a regular grid of site positions.
Irregularity of one corresponds to the maximum 'randomness' of cell positions within the grid, so that the grid is not visible.

A shader based on Voronoi noise. The white value of the shader is based on the distance in UV space from the shaded point to the nearest Voronoi site. Irregularity = 0.2.

A shader based on Voronoi noise. The white value of the shader is based on the distance in UV space from the shaded point to the nearest Voronoi site. Irregularity = 0.8.
Similar to above, but takes a 3d vector and returns the nearest Voronoi site in 3d.
Advanced Fractional Brownian Motion Noise
This fbm function is a more general fbm that takes more parameters.
basis_type selects from a number of basis noise functions:
0: Perlin basis
1: Ridged basis
2: Voronoi basis
x is a 3-vector at which the noise is evaluated.
H controls the fractal dimension: a larger value causes faster attenuation of higher frequencies.
A good default value is 1.
Lacunarity determines the gap in frequencies between different 'octaves' of noise.
A larger lacunarity means each subsequence octave will have higher frequency.
A good default value is 2.
Octaves determines the number of octaves of noise that are added together. If the value has a fractional component, the last octave is attenuated by the fractional part then added.
Basis Types

Perlin basis, 1 octave
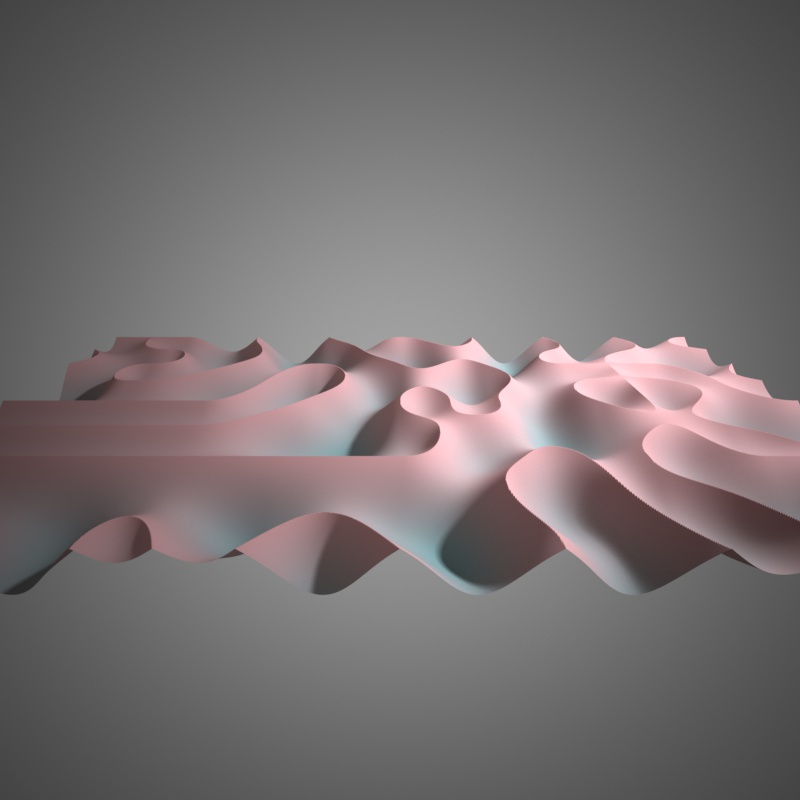
Ridged basis, 1 octave

Voronoi basis, 1 octave
Effect of number of octaves

Perlin basis, 1 octave

Perlin basis, 2 octaves

Perlin basis, 3 octaves

Perlin basis, 10 octaves

Ridged basis, 1 octave
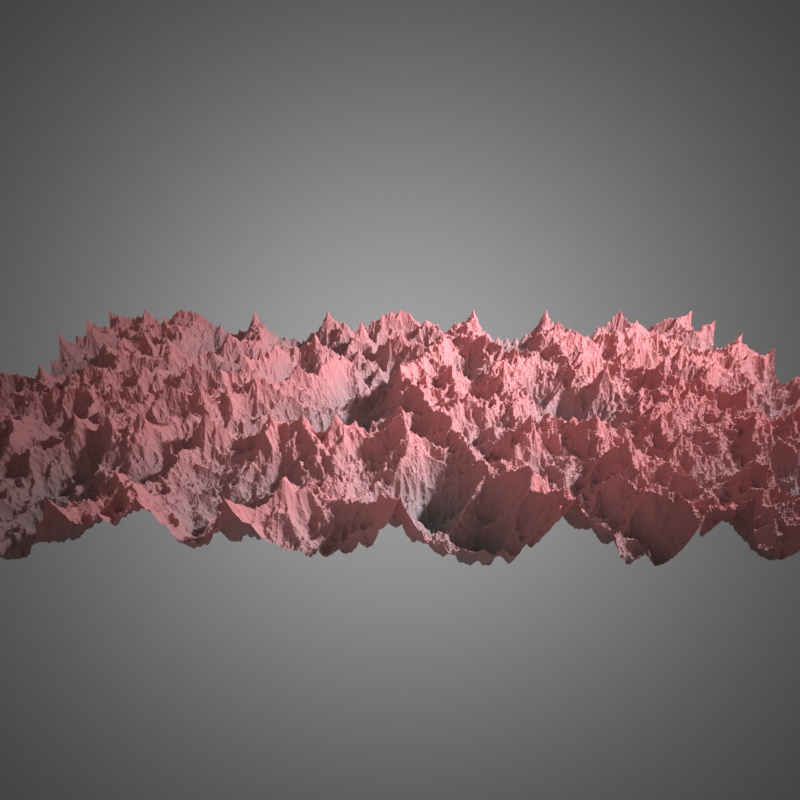
Ridged basis, 10 octaves

Voronoi basis, 1 octave
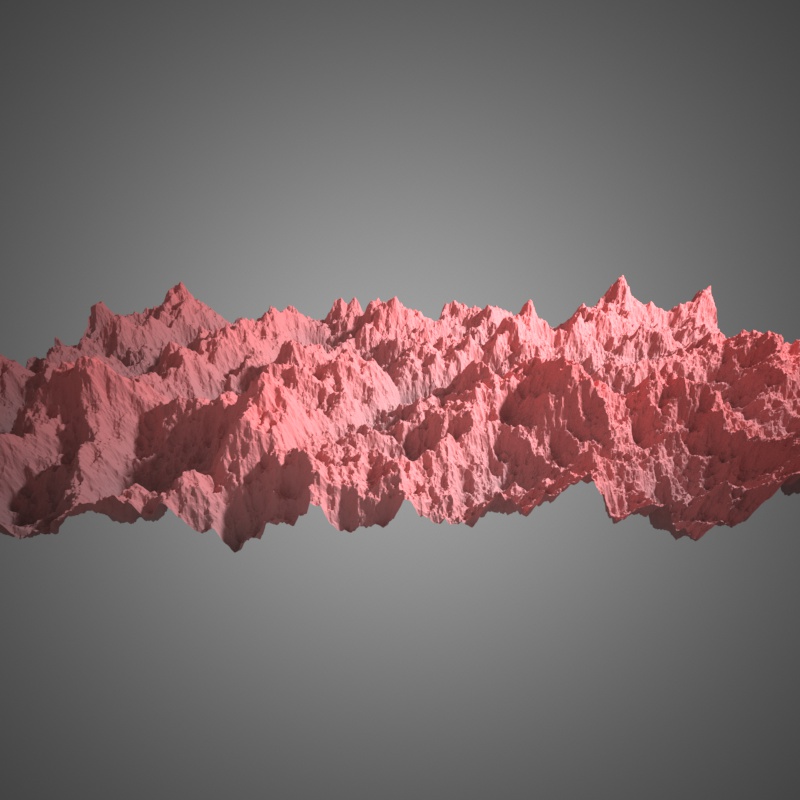
Voronoi basis, 10 octaves
Effect of fractal dimension (H)
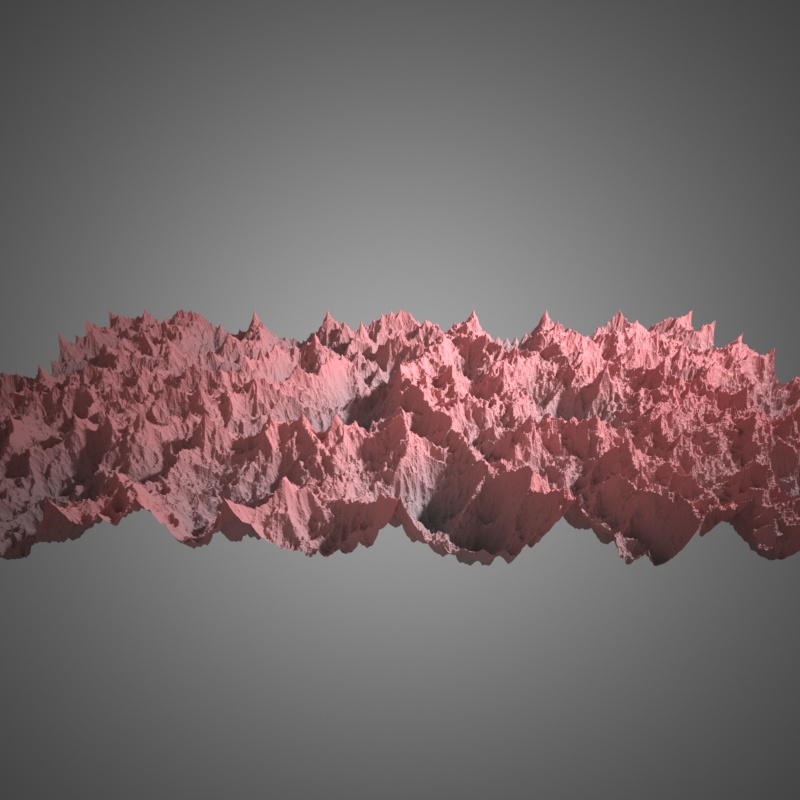
Ridged basis, H=1
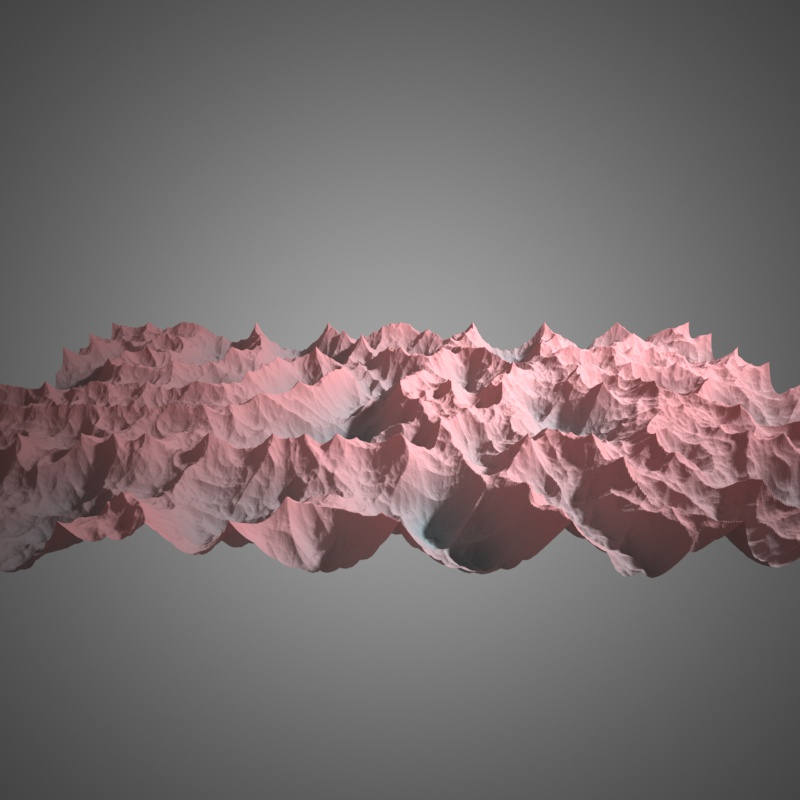
Ridged basis, H=1.5
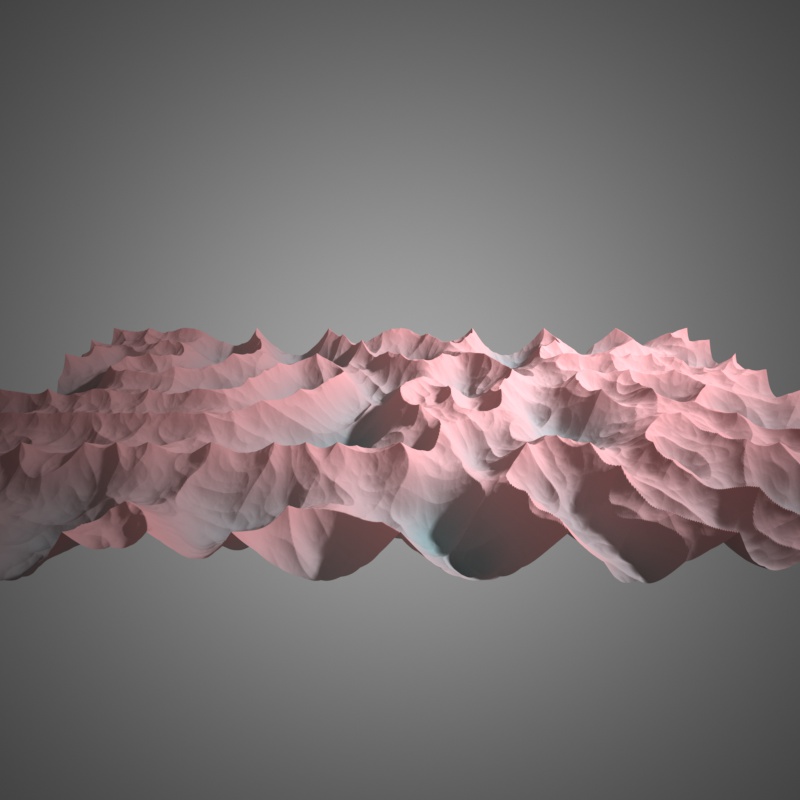
Ridged basis, H=2
Effect of Lacunarity

Ridged basis, lacunarity = 3

Ridged basis, lacunarity = 4

Ridged basis, lacunarity = 6
You can download the example Indigo scene used in the images above here.