Texture Maps
Texture maps are a standard way of adding fine surface detail without adding more geometry. Indigo supports texture maps in many file formats, which are listed here.
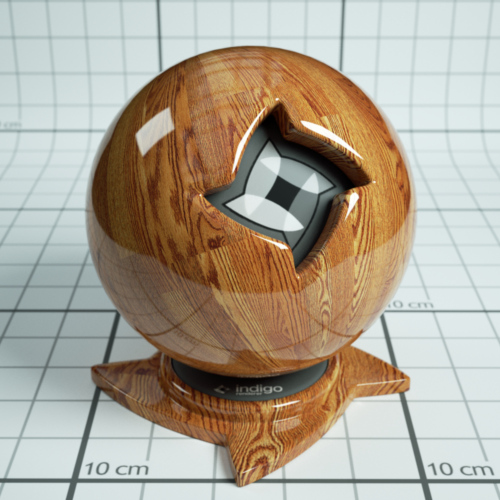
An example Phong material with a wood texture applied.
Supported texture formats:
| JPEG | .JPG .JPEG | Greyscale, RGB and CMYK are supported. |
| PNG | .PNG | Greyscale, greyscale with alpha, RGB and RGBA are supported. 8 bits per channel and 16 bits per channel supported. |
| Truevision Targa | .TGA | Greyscale (8 bits per pixel) and RGB (24 bits per pixel) are supported. |
| Windows Bitmap | .BMP | Greyscale (8 bits per pixel) and RGB (24 bits per pixel) are supported. Compressed BMP files are not supported. |
| OpenEXR | .EXR | 16 bits per channel and 32 bits per channel are supported. |
| TIFF | .TIF .TIFF | Greyscale, RGB, RGBA are supported. 8 bits per channel and 16 bits per channel supported. |
| GIF | .GIF | Supported. Gif animation is not supported. |
| RGBE | .HDR | Supported. |
Additional options:
| UV set index | Index of the set of uv coordinates used for texture maps. Usually generated by your 3D modelling package. |
| Path | Path to the texture map on disk. The path must either be absolute, or relative to the scene's working directory. |
| Gamma (exponent) | Used for converting non-linear RGB values (e.g. sRGB) to linear intensity values. A typical value is 2.2, corresponding to the sRGB standard. |
ABC values / texture adjustments
Often you'll want to change a texture's brightness or contrast in the rendered image, without having to modify the texture map itself.
During rendering, Indigo modifies the source texture data according to a quadratic formula with 3 parameters, A, B and C:
y = ax² + bx + c
x is the input value from the texture map, and y is the output value.
As a quick example for how this equation works: If we use A = 0, B = 1, C = 0 then the value is completely unchanged; this is therefore also the default.
A value – Quadratic
The A value scales the contribution of the quadratic (x²) term. This is typically not used, however it can be useful to adjust the contrast of a texture, with a value greater than 0, and/or a negative C value.
B value - Scale/Multiplier

Texture Scale (B value) of 2.
The B value scales the contribution of the linear (x) term. This is typically used to adjust the overall brightness (for example to reduce the maximum albedo of a texture, using a value of 0.8 or so), and can also be useful to adjust the contrast of a texture, with a value greater than 1, and/or a negative C value.
C value – Base/Constant

Texture constant (C value) of 0.2.
The C value is always added, regardless of the input texture amount; it therefore acts as a base or "floor" value. So for example if you have a completely black texture, and a C value of 0.5, it would appear as 50% grey.